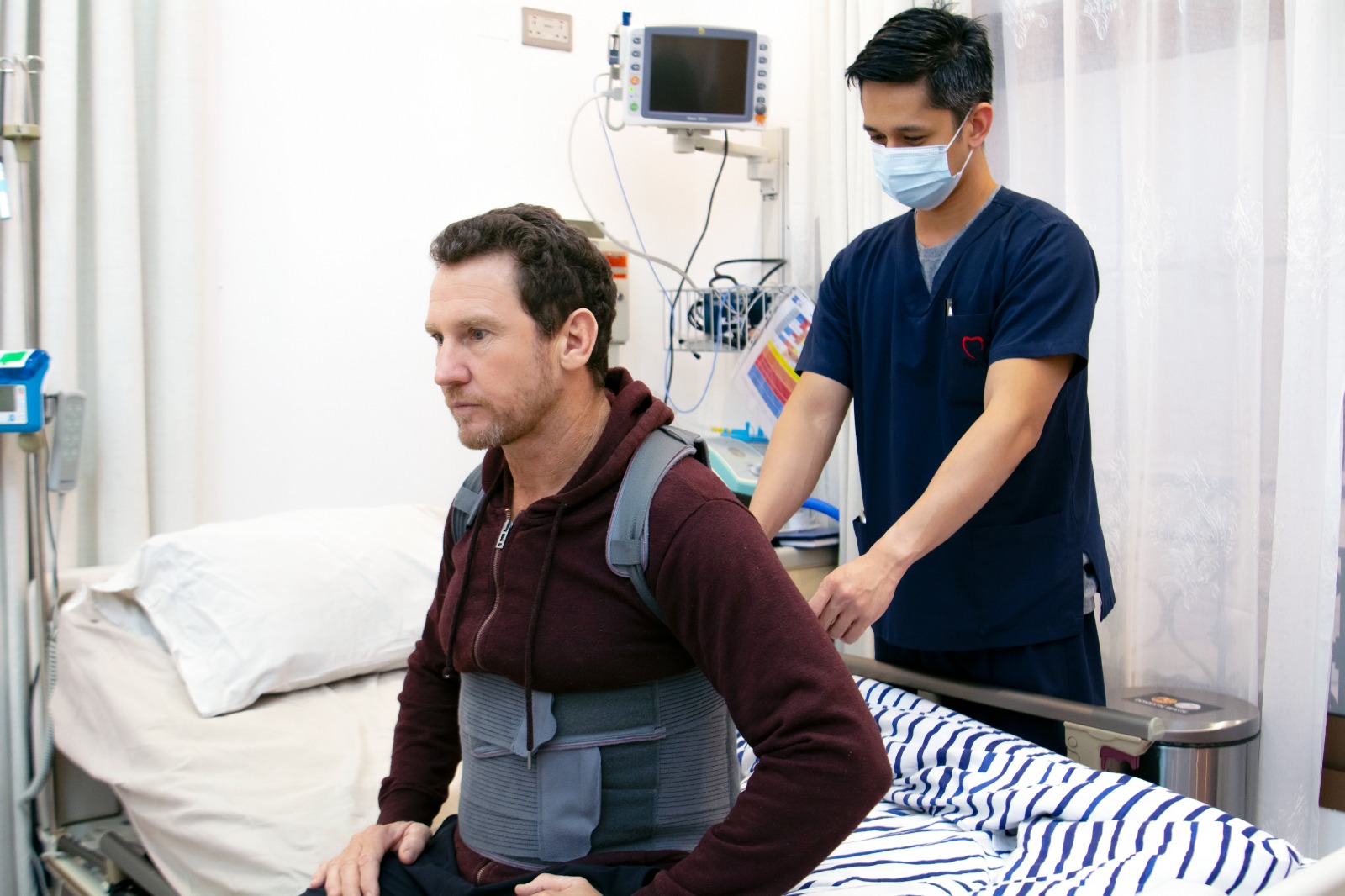
A stroke can alter life in an instant, leaving survivors and families facing an uncertain journey. While the effects can range from muscle weakness, and difficulty walking to swallowing difficulties and cognitive changes, the right rehabilitation approach offers hope.
Rehabilitation is not just about regaining lost movement – it’s about rebuilding independence, confidence, and overall well-being. The most effective recovery happens through interdisciplinary care where multiple healthcare professionals work together toward shared goals.
Interdisciplinary Stroke Rehabilitation: A Team Effort
Post-stroke care thrives when specialists combine their expertise to address all aspects of recovery. The core team often includes:
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (PMR) Physician/Physiatrist: Leads the rehabilitation program, ensuring medical stability and functional progress. They manage pain, spasticity, bladder and bowel issues, depression, and medical complications such as pressure injuries, deep vein thrombosis, and contractures. They coordinate the care plan and liaise between all team members.
- Physiotherapists: Focus on motor recovery, strength, balance, and mobility through tailored exercise and gait training.
- Occupational Therapists: Help patients regain independence in daily activities such as dressing, eating and home management.
- Speech and Language Therapists: Address speech, language, cognition, and swallowing difficulties.
- Psychologists: Support mental health, coping strategies, and reintegration into community life.
- Dietitians: Ensure optimal nutrition for recovery, addressing swallowing-related modifications, weight management, hydration, and specialized diets for conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or high cholesterol to reduce secondary stroke risk.
- Nurses: Provide medical monitoring, medication administration, and patient/family education.
This collaborative approach ensures that every aspect of recovery – physical, medical, nutritional, and emotional – is addressed.
The Importance of Early Rehabilitation
Timing matters. Initiating rehabilitation within 24 – 48 hours after medical stabilization can significantly improve long-term outcomes. Early intervention:
- Prevents complications like muscle atrophy, joint stiffness, and blood clots.
- Maintains range of motion and muscle strength.
- Builds confidence and motivation early in recovery.
Key Rehabilitation Strategies
- Harnessing Neuroplasticity
The brain has the remarkable ability to reorganize and form new pathways after injury – a process called neuroplasticity. Therapies stimulate this process through:
- Cortical remapping: healthy brain areas take over lost functions.
Repetitive task training: practicing everyday activities (e.g. standing from a chair) to re-establish skills.
- Axonal sprouting: encouraging surviving neurons to form new connections.
- Regaining Strength and Mobility
Stroke rehabilitation restores movement through:
- Motor-skill exercises: for walking, balance, and swallowing
- Range-of-motion therapy: reduces spasticity and stiffness
- Functional retraining: improves independence in daily tasks
- Improving Balance and Preventing Falls
- Weight shifting exercises: enhance body awareness and adaptability
- Core stabilization: improves postures and reduces fall risk
- Assistive devices: canes, walkers, and orthotics when needed
- Addressing Stiffness and Spasticity
Spasticity management is essential to prevent contractures and improve comfort:
- Daily stretching and positioning programs
- Splints/braces to prevent joint stiffness
- Manual therapy and targeted interventions
- Physiatrist-led options: oral medications, botulinum injections, or nerve blocks
- Leveraging Advanced Technology
Modern rehabilitation integrates innovative tools to enhance recovery:
- Robotic assisted therapy: Guides repetitive movement to reinforce motor learning
- Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): Activates muscles with gentle electrical impulse
- Virtual Reality (VR): Immersive environments that motivate and challenge patients.
Manging Medical Complications Post-Stroke
Stroke recovery is not only about physical function. The PMR physician plays a critical role in:
- Pain management: shoulder pain, joint pain, neuropathic discomfort
- Bladder and bowel care: preventing infections, constipation, and incontinence
- Support mental health: identify and treat post-stroke depression, anxiety, and emotional lability, often in collaboration with the psychologist.
- Secondary prevention: managing risk factors to reduce the chance of another stroke
A Holistic Focus on Patient Well-being
True recovery goes beyond the body – it restores a person’s sense of self and purpose. This includes:
- Setting achievable goals
- Celebrating small victories
- Supporting mental health and emotional resilience
- Empowering patients to participate actively in their care
Your Recovery Journey Starts Here
At NMC Provita, our PMR physicians, therapists, nurses, psychologists and dietitians work together to deliver customized rehabilitation programs. Whether you need advanced spasticity management, innovative mobility training, or emotional support, our team is with you every step of the way.
Recovery after stroke is possible – and with the right interdisciplinary care, it can be life changing.
Schedule a Visit Today 8008020